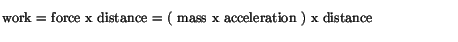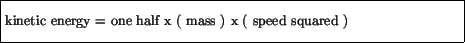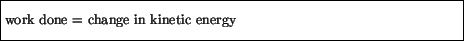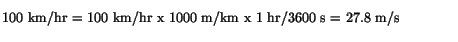The advantage of electric vehicles is to reduce carbon emissions and these can be charged at home and if you are lucky may even be charged by a solar panel on your roof. Excellent.
But some hybrids do not have a home charger socket and also no way of switching on to electric only when in city centres.
Can someone please explain to me how these hybrids can be more efficient than an identical none electric car which does not have to carry an extra battery etc?