Whenever transitioning from a preceding supply cable protected by a higher current circuit breaker or fuse, I always fuse down before connecting the appropriate lower gauge wire.
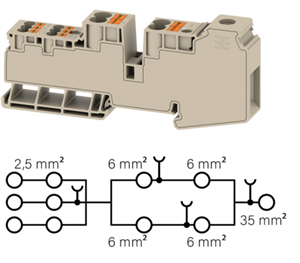
What I wonder is then how such distribution blocks like these Weidmüller AWPD 35 4X6/6X2.5 are safe: