The IET regulations require that the resistance of the conductors, including the resistance of the connections, between the terminals for the protective conductor of socket-outlets and of fixed equipment or any extraneous-conductive-parts and the equipotential bonding busbar (EBB) shall not exceed 0.2 Ω.
However the cable connection between the EBB and the Main Distribution board, is not defined, (identified in red in the image below) - either in terms of:
1 - maximum resistance
2 - minimum cable size
3 - if the cable needs to connect to the distribution board that serves the room or should go back to the Main distribution board.
4 - if there are number of EBB's can they be connected by a single cable in a daisy chain arrangement back to the distribution board.
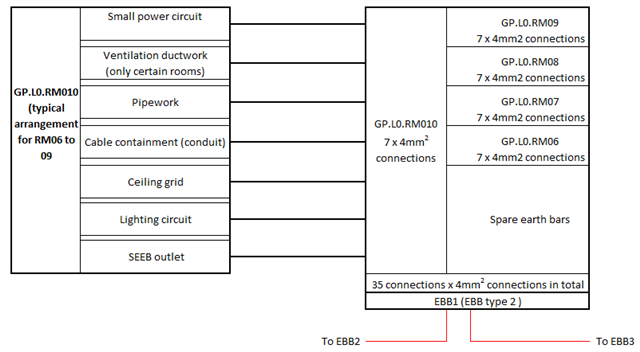
Is any able to provide guidance on the four questions above?